FAQ
Most common things an IT person Should Know

As the name implies, ransomware is a type of malware that demands some form of payment from the victim in order to recover control of their computer and/or data. Within that broad definition, there are a few twists and turns that are worth noting.
First, there are variants with regard to exactly what the victim is being held to ransom for. Typically, the attacker encrypts files on the victim’s computer in such a way that they cannot be opened unless the victim has a decryption key. Access to the decryption key is what the attacker wants the victim to pay for.
.
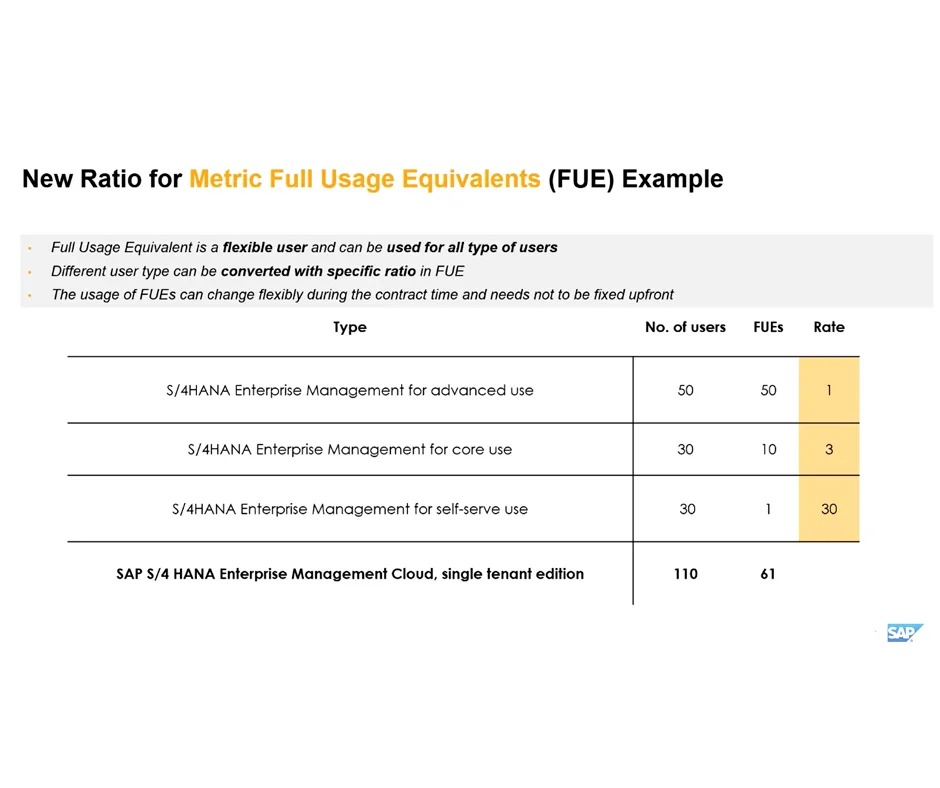
Full User Equivalents (FUE) are individuals who are authorized to use the Cloud Service. The number of FUE subscribed by Customer is stated in the Order Form. Full User Equivalent is defined by the table below. Use rights descriptions are set forth in the SAP Software Use Rights document.
Conversion ratio into FUE Use Rights
0.5 SAP Developer Access
1 S/4HANA Enterprise Management for Professional use
5 S/4HANA Enterprise Management for Functional use
50 S/4HANA Enterprise Management for Productivity use

The Internet of Things (IoT) is growing exponentially, but security for IoT projects and deployments remains an obstacle for many organizations. One fundamental IoT security component is making sure devices and services have trusted identities that can interact within secure ecosystems.
This puts you and everyone else at risk: from unwittingly being spied on or having your data compromised to being unable to lock your own home. You could even become part of a botnet that attacks the Internet. Your insecure webcam – along with millions of others – could be used to attack the power grid of an entire country.
From dental sensors that can monitor what a person eats to kitty litters that can track a cat’s every movement, it can be difficult to sort fact from fiction when it comes to the Internet of Things. Can you tell which is real and which is not?

i The term Industry 5.0 refers to people working with robots and smart machines. It is about robots helping humans work faster by leveraging advanced technologies such as big data analytics.
ii. Industry 5.0 is termed as the revolution in which man and machine are findings ways to work for improvement means and efficiency of the manufacturing production .
iii. Ocicka and Turek suggested that Industry 5.0 is compelled with various industries technologists, philosophies, and others to focus on the human factors and technologies in the manufacturing systems.
iv. Industry 5.0 is considered the edge of the smart factory, where it communicates with robots and humans . It uses social networks for communication purposes among humans and electronics components.

Solar geoengineering, or solar radiation modification (SRM), is a type of climate engineering in which sunlight (solar radiation) would be reflected back to outer space to limit or reverse human-caused climate change.It is not a substitute for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but would act as a temporary measure to limit warming while emissions of greenhouse gases are reduced and carbon dioxide is removed. The most studied methods of SRM are stratospheric aerosol injection and marine cloud brightening.
Solar geoengineering appears able to prevent some or much of climate change temperature increases. Climate models consistently indicate that it is capable of returning global, regional, and local temperatures and precipitation closer to pre-industrial levels. Solar geoengineering's principal advantages are the speed with which it could be deployed and become active and the reversibility of its direct climatic effects, although the latter varies depending on method, with some concerns raised over stratospheric aerosol injection.
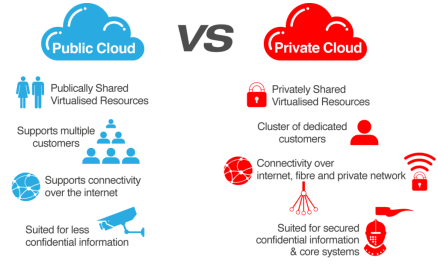
Public cloud is a type of computing where resources are offered by a third-party provider via the internet and shared by organizations and individuals who want to use or purchase them. Some public cloud computing resources are available for free, while customers may pay for other resources through subscription or pay-per-usage pricing models.
From artificial intelligence services and developer tools to the storage and computing capacity for virtually any workload, public cloud helps companies to harness cutting-edge technologies and achieve global scale without shouldering the costs and labor themselves.
Public clouds contrast with private cloud models, where the resources are available only to a single organization and the data center is managed either on-premises or off-site by a vendor. For organizations looking for an alternative to traditional on-premises IT architectures or other types of cloud computing, the public cloud offers nearly infinite scalability and self-service provisioning to meet workload and user demands.
Private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single customer. It combines many of the benefits of cloud computing with the security and control of on-premises IT infrastructure.
Private cloud (also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud) is a cloud computing environment in which all hardware and software resources are dedicated exclusively to, and accessible only by, a single customer. Private cloud combines many of the benefits of cloud computing—including elasticity, scalability, and ease of service delivery—with the access control, security, and resource customization of on-premises infrastructure.
By building private cloud architecture according to cloud native principles, an organization gives itself the flexibility to easily move workloads to public cloud or run them within a hybrid cloud (mixed public and private cloud) environment whenever they’re ready.
